Exploring pre-service teachers’ generative AI readiness and behavioral intentions
A pilot study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31129/LUMAT.13.1.2755Keywords:
generative AI, teacher education, preservice teacher, technological adoptionAbstract
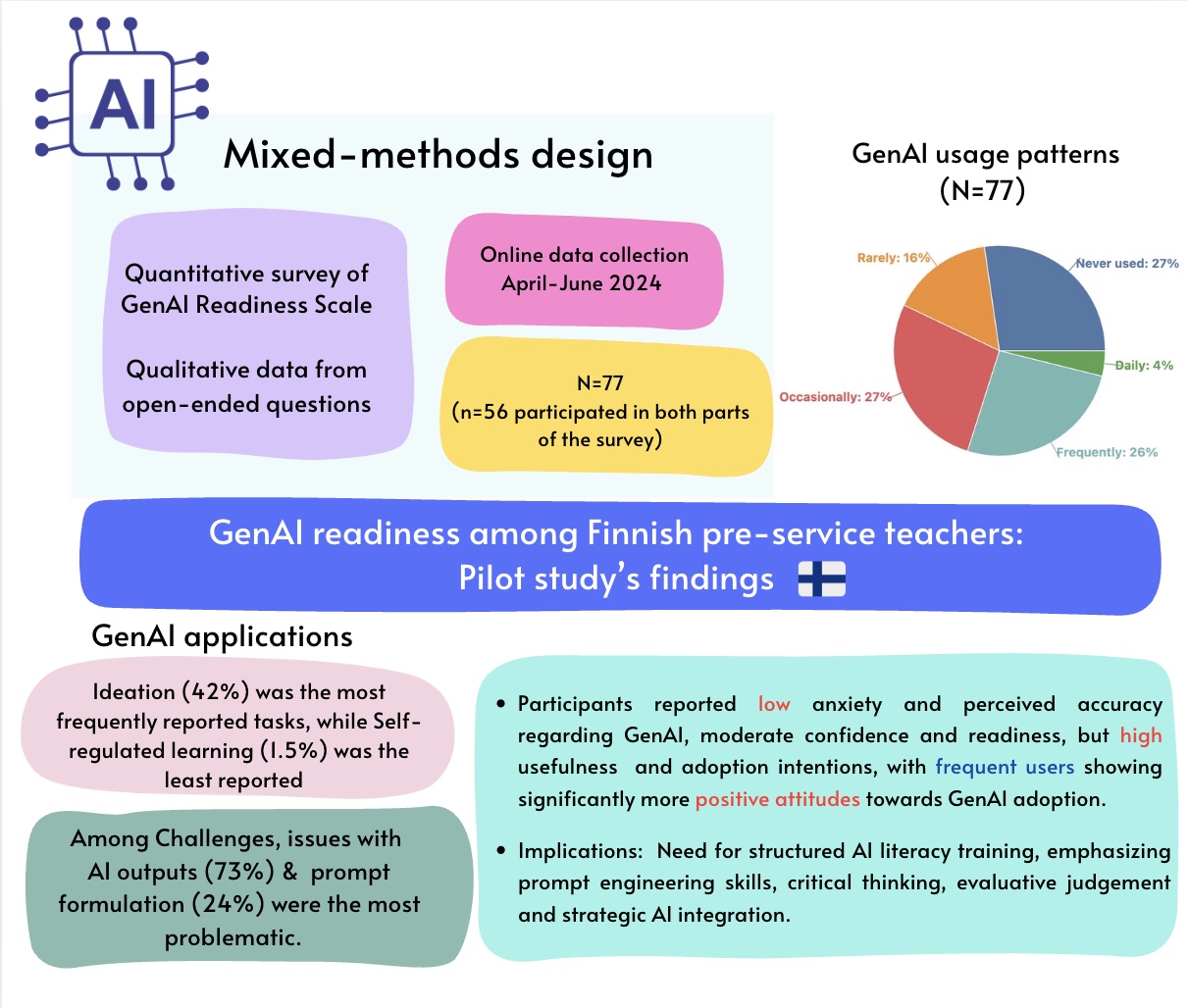
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has rapidly emerged as a field capable of creating unique content across various areas. While offering significant potential, it presents challenges including ethical concerns, content inaccuracies, and increased challenges for educators who must adapt to fast-evolving technologies. Integrating GenAI tools into teacher education represents an urgent global research priority. This pilot study explores GenAI readiness, experiences, perceptions, and behavioral intentions among Finnish pre-service teachers while examining the feasibility of the GenAI Readiness Scale as a measurement instrument. Using a mixed-methods approach combining quantitative survey data (N=77) with qualitative responses (n=56) from open-ended questions, the research provides a nuanced analysis of future educators’ positioning toward GenAI integration in educational settings. Findings reveal a significant adoption gap, with 27% of participants never used GenAI tools as of April-June 2024, while majority engaged sporadically. Despite low perceived accuracy, frequent users continued utilizing GenAI, suggesting that usability, efficiency, and creative support outweigh accuracy concerns. Ideation and content creation emerged as the most common GenAI-supported tasks, while self-regulated and adaptive learning remained underutilized, indicating limited awareness of GenAI’s broader potential. Challenges primarily involved output quality and prompting difficulties. Participants preferred modifying AI outputs rather than refining prompts, employing strategies like output modification and external verification, though critical evaluation wasn’t always explicit. These findings highlight the need for structured AI literacy training in teacher education, emphasizing prompt engineering, evaluative judgment, and strategic AI integration. This study underscores the importance of developing GenAI competencies among pre-service teachers to ensure effective, responsible, and pedagogically meaningful AI adoption. Future research should explore longitudinal adoption trends, and impact of AI literacy training on teaching and learning practices.
References
Ayanwale, M. A., Sanusi, I. T., Adelana, O. P., Aruleba, K. D., & Oyelere, S. S. (2022). Teachers’ readiness and intention to teach artificial intelligence in schools. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 3, 100099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100099 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100099
Aydın, Ö., & Karaarslan, E. (2022). OpenAI ChatGPT Generated Literature Review: Digital Twin in Healthcare. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4308687 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4308687
Bick, A., Blandin, A., & Deming, D. (2024). The Rapid Adoption of Generative AI (No. w32966; p. w32966). National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w32966 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3386/w32966
Bommasani, R., Hudson, D. A., Adeli, E., Altman, R., Arora, S., von Arx, S., Bernstein, M. S., Bohg, J., Bosselut, A., Brunskill, E., Brynjolfsson, E., Buch, S., Card, D., Castellon, R., Chatterji, N., Chen, A., Creel, K., Davis, J. Q., Demszky, D., … Liang, P. (2021). On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models (Version 3). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2108.07258
Botana, F., & Recio, T. (2024). Geometric Loci and ChatGPT: Caveat Emptor! Computation, 12(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12020030 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12020030
Brown, H., Lee, K., Mireshghallah, F., Shokri, R., & Tramèr, F. (2022). What Does it Mean for a Language Model to Preserve Privacy? 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, 2280–2292. https://doi.org/10.1145/3531146.3534642 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3531146.3534642
Bui, P., Pongsakdi, N., McMullen, J., & Veermans, M. (2024). Affordances, Challenges, and Opportunities of ChatGPT in Mathematics Education: A Scoping Review. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ce2ky DOI: https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ce2ky
Casey, J. E., Kirk, J., Kuklies, K., & Mireles, S. V. (2023). Using the technology acceptance model to assess how preservice teachers’ view educational technology in middle and high school classrooms. Education and Information Technologies, 28(2), 2361–2382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11263-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11263-6
Casey, J. E., Pennington, L. K., & Mireles, S. V. (2021). Technology Acceptance Model: Assessing Preservice Teachers’ Acceptance of Floor-Robots as a Useful Pedagogical Tool. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 26(3), 499–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-020-09452-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-020-09452-8
Celik, I., Dindar, M., Muukkonen, H., & Järvelä, S. (2022). The promises and challenges of artificial intelligence for teachers: A systematic review of research. TechTrends, 66(4), 616–630. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-022-00715-y
Dai, Y., Chai, C.-S., Lin, P.-Y., Jong, M. S.-Y., Guo, Y., & Qin, J. (2020). Promoting Students’ Well-Being by Developing Their Readiness for the Artificial Intelligence Age. Sustainability, 12(16), 6597. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166597 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166597
Darmansyah, D., Fianto, B. A., Hendratmi, A., & Aziz, P. F. (2021). Factors determining behavioral intentions to use Islamic financial technology: Three competing models. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 12(4), 794–812. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-12-2019-0252 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/JIMA-12-2019-0252
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Eisbach, S., Langer, M., & Hertel, G. (2023). Optimizing human-AI collaboration: Effects of motivation and accuracy information in AI-supported decision-making. Computers in Human Behavior: Artificial Humans, 1(2), 100015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chbah.2023.100015
European Commission. Directorate General for Education, Youth, Sport and Culture. (2022). Ethical guidelines on the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and data in teaching and learning for educators. Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2766/153756
Farjon, D., Smits, A., & Voogt, J. (2019). Technology integration of pre-service teachers explained by attitudes and beliefs, competency, access, and experience. Computers & Education, 130, 81–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.11.010 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.11.010
Getenet, S. (2024). Pre-service teachers and ChatGPT in multistrategy problem-solving: Implications for mathematics teaching in primary schools. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 19(1), em0766. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/14141 DOI: https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/14141
Haman, M., & Školník, M. (2023). Using ChatGPT to conduct a literature review. Accountability in Research, 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989621.2023.2185514 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08989621.2023.2185514
Hodge-zickerman, A., & York, C. (2024). Embracing ChatGPT in the Evolving Landscape of Mathematics Teacher Education and Assessment. Exploring New Horizons: Generative Artificial Intelligence and Teacher Education, 111.
Kaplan-Rakowski, R., Grotewold, K., Hartwick, P., & Papin, K. (2023). Generative AI and teachers’ perspectives on its implementation in education. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 34(2), 313–338. DOI: https://doi.org/10.70725/815246mfssgp
Kreijns, K., Kirschner, P. A., Jochems, W., & Van Buuren, H. (2007). Measuring perceived sociability of computer-supported collaborative learning environments. Computers & Education, 49(2), 176–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2005.05.004 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2005.05.004
Latif, E., & Zhai, X. (2024). Fine-tuning ChatGPT for automatic scoring. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 6, 100210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2024.100210 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2024.100210
Law, L. (2024). Application of generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) in language teaching and learning: A scoping literature review. Computers and Education Open, 6, 100174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeo.2024.100174 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeo.2024.100174
Lee, J. D., & See, K. A. (2004). Trust in Automation: Designing for Appropriate Reliance. Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, 46(1), 50–80. https://doi.org/10.1518/hfes.46.1.50_30392 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1518/hfes.46.1.50.30392
Li, J., & Huang, J.-S. (2020). Dimensions of artificial intelligence anxiety based on the integrated fear acquisition theory. Technology in Society, 63, 101410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101410 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101410
Li, P.-H., Lee, H.-Y., Cheng, Y.-P., Starčič, A. I., & Huang, Y.-M. (2023). Solving the Self-regulated Learning Problem: Exploring the Performance of ChatGPT in Mathematics. In Y.-M. Huang & T. Rocha (Eds.), Innovative Technologies and Learning (Vol. 14099, pp. 77–86). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-40113-8_8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-40113-8_8
Lim, W. M., Gunasekara, A., Pallant, J. L., Pallant, J. I., & Pechenkina, E. (2023). Generative AI and the future of education: Ragnarök or reformation? A paradoxical perspective from management educators. The International Journal of Management Education, 21(2), 100790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100790 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100790
Liu, Y., & Wang, H. (2024). Who on Earth Is Using Generative AI? DOI: https://doi.org/10.1596/1813-9450-10870
Lo, C. K., Hew, K. F., & Jong, M. S. (2024). The influence of ChatGPT on student engagement: A systematic review and future research agenda. Computers & Education, 219, 105100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2024.105100 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2024.105100
Lodge, J. M., Yang, S., Furze, L., & Dawson, P. (2023). It’s not like a calculator, so what is the relationship between learners and generative artificial intelligence? Learning: Research and Practice, 9(2), 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/23735082.2023.2261106 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/23735082.2023.2261106
MacCallum, R. C., Widaman, K. F., Zhang, S., & Hong, S. (1999). Sample size in factor analysis. Psychological Methods, 4(1), 84–99. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.4.1.84 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1037//1082-989X.4.1.84
Mai, D. T. T., Da, C. V., & Hanh, N. V. (2024). The use of ChatGPT in teaching and learning: A systematic review through SWOT analysis approach. Frontiers in Education, 9, 1328769. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1328769 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1328769
Manohar, N., Prasad, S. S., & Pise, G. (2024). ChatGPT: The Good, The Bad, and Everything in Between. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 15(1), 166–168. https://doi.org/10.4103/idoj.idoj_274_23 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/idoj.idoj_274_23
Martin, F., Zhuang, M., & Schaefer, D. (2024). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence in K-12 education (2017–2022). Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 6, 100195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100195 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100195
Mehrabi, N., Morstatter, F., Saxena, N., Lerman, K., & Galstyan, A. (2022). A Survey on Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning. ACM Computing Surveys, 54(6), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1145/3457607 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3457607
Mishra, P., Warr, M., & Islam, R. (2023). TPACK in the age of ChatGPT and Generative AI. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 39(4), 235–251. https://doi.org/10.1080/21532974.2023.2247480 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/21532974.2023.2247480
Mittal, U., Sai, S., & Chamola, V. (2024). A comprehensive review on generative ai for education. IEEE Access. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3468368
Moorhouse, B. L. (2024). Beginning and first-year language teachers’ readiness for the generative AI age. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 6, 100201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2024.100201 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2024.100201
Naeem, M., Ozuem, W., Howell, K., & Ranfagni, S. (2023). A Step-by-Step Process of Thematic Analysis to Develop a Conceptual Model in Qualitative Research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 22, 16094069231205789. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069231205789 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069231205789
Nguyen, H. A., Stec, H., Hou, X., Di, S., & McLaren, B. M. (2023). Evaluating ChatGPT’s Decimal Skills and Feedback Generation in a Digital Learning Game. In O. Viberg, I. Jivet, P. J. Muñoz-Merino, M. Perifanou, & T. Papathoma (Eds.), Responsive and Sustainable Educational Futures (Vol. 14200, pp. 278–293). Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42682-7_19 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42682-7_19
Okonkwo, C. W., & Ade-Ibijola, A. (2021). Chatbots applications in education: A systematic review. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 2, 100033. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2021.100033
OpenAI. (2024). GPT-4. https://openai.com/index/gpt-4-research/
Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. T., Glazewski, K. D., Newby, T. J., & Ertmer, P. A. (2010). Teacher value beliefs associated with using technology: Addressing professional and student needs. Computers & Education, 55(3), 1321–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.06.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.06.002
Oxman, S., Wong, W., & Innovations, D. (2014). White paper: Adaptive learning systems. Integrated Education Solutions, 6–7.
Parker, K. R., & Davey, B. (2014). Computers in schools in the USA: A social history. Reflections on the History of Computers in Education: Early Use of Computers and Teaching about Computing in Schools, 203–211. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-55119-2_14
Parra, V., Sureda, P., Corica, A., Schiaffino, S., & Godoy, D. (2024). Can Generative AI Solve Geometry Problems? Strengths and Weaknesses of LLMs for Geometric Reasoning in Spanish. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 8(5), 65. https://doi.org/10.9781/ijimai.2024.02.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.9781/ijimai.2024.02.009
Puerta-Beldarrain, M., Gómez-Carmona, O., Sánchez-Corcuera, R., Casado-Mansilla, D., López-de-Ipiña, D., & Chen, L. (2025). A multifaceted vision of the Human-AI collaboration: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access, 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3536095 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3536095
Schellaert, W., Martínez-Plumed, F., Vold, K., Burden, J., A. M. Casares, P., Sheng Loe, B., Reichart, R., Ó hÉigeartaigh, S., Korhonen, A., & Hernández-Orallo, J. (2023). Your Prompt is My Command: On Assessing the Human-Centred Generality of Multimodal Models. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 77, 377–394. https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.1.14157 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.1.14157
Selwyn, N. (2019). Should robots replace teachers?: AI and the future of education. John Wiley & Sons.
Stryker, C., & Scapicchio, M. (2024, March 22). What is Generative AI? Https://Www.Ibm.Com. https://www.ibm.com/topics/generative-ai
Tai, J., Ajjawi, R., Boud, D., Dawson, P., & Panadero, E. (2018). Developing evaluative judgement: Enabling students to make decisions about the quality of work. Higher Education, 76(3), 467–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-017-0220-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-017-0220-3
Tankelevitch, L., Kewenig, V., Simkute, A., Scott, A. E., Sarkar, A., Sellen, A., & Rintel, S. (2024). The Metacognitive Demands and Opportunities of Generative AI. Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1145/3613904.3642902 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3613904.3642902
Tondeur, J., Van Braak, J., Sang, G., Voogt, J., Fisser, P., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. (2012). Preparing pre-service teachers to integrate technology in education: A synthesis of qualitative evidence. Computers & Education, 59(1), 134–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.10.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.10.009
Tondeur, J., Van Braak, J., Siddiq, F., & Scherer, R. (2016). Time for a new approach to prepare future teachers for educational technology use: Its meaning and measurement. Computers & Education, 94, 134–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.11.009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.11.009
Van Der Linden, S. (2022). Misinformation: Susceptibility, spread, and interventions to immunize the public. Nature Medicine, 28(3), 460–467. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01713-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01713-6
Van Katwijk, L., Jansen, E., & Van Veen, K. (2023). Pre-service teacher research: A way to future-proof teachers? European Journal of Teacher Education, 46(3), 435–455. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2021.1928070 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2021.1928070
Van Twillert, A., Kreijns, K., Vermeulen, M., & Evers, A. (2020). Teachers’ beliefs to integrate Web 2.0 technology in their pedagogy and their influence on attitude, perceived norms, and perceived behavior control. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 1, 100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100014 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100014
Venkatesh, V., & Bala, H. (2008). Technology Acceptance Model 3 and a Research Agenda on Interventions. Decision Sciences, 39(2), 273–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5915.2008.00192.x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5915.2008.00192.x
Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A Theoretical Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model: Four Longitudinal Field Studies. Management Science, 46(2), 186–204. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.46.2.186.11926 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.46.2.186.11926
Wang, S., Yu, H., Hu, X., & Li, J. (2020). Participant or spectator? Comprehending the willingness of faculty to use intelligent tutoring systems in the artificial intelligence era. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51(5), 1657–1673. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12998 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12998
Wang, Y.-M. (2002). When Technology Meets Beliefs: Preservice Teachers’ Perception of the Teacher’s Role in the Classroom with Computers. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 35(1), 150–161. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2002.10782376 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2002.10782376
Ye, X., Liu, P.-F., Lee, X.-Z., Zhang, Y.-Q., & Chiu, C.-K. (2021). Classroom misbehaviour management: An SVVR-based training system for preservice teachers. Interactive Learning Environments, 29(1), 112–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1579235 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1579235
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Phuong Bui, Tiina Korhonen, Sini Kontkanen, Sorella Karme, Satu Piispa-Hakala, Marjaana Veermans

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









