Navigating challenges in teaching the tower problem
Pre-service teachers' learning experiences of problem-solving through the lens of TDS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31129/LUMAT.14.1.2800Keywords:
mathematics problem-solving, algebra, teacher education, TDS, interventionAbstract
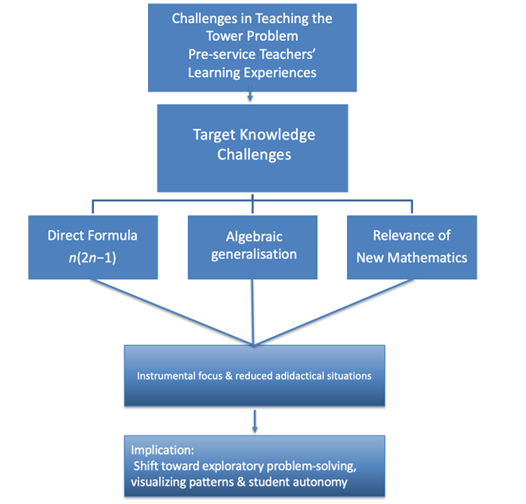
This study highlights the challenges faced by pre-service teachers in navigating mathematics problem-solving instruction at the university level. The activity of problem-solving is central to mathematical sense-making, crucial from the elementary grades onward. However, problem-solving often occupies a marginalised position in elementary school classrooms. This issue can be partly attributed to the fact that many pre-service elementary teachers possess (1) limited mathematical knowledge regarding problem-solving strategies and (2) counterproductive beliefs about how to effectively teach these skills. Building on an intervention with a group of pre-service elementary teachers addressing these two critical barriers to teaching problem-solving, this study explores the challenges that these teachers identified as they prepared and delivered lessons focused on problem-solving. Drawing on the Theory of Didactical Situations (TDS), key concepts were employed to analyze the data with a focus on the target knowledge. The findings add to the growing body of research highlighting challenges that teacher education programs can address to better prepare pre-service teachers for teaching problem-solving in mathematics.
References
Ambrose, R. (2004). Initiating change in pre-service teachers’ orientations to mathematics teaching by building on beliefs. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 7, 91–119. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMTE.0000021879.74957.63 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMTE.0000021879.74957.63
Artigue, M. (2014). Potentialities and limitations of the Theory of Didactic Situations for addressing the teaching and learning of mathematics at university level. Research in Mathematics Education, 16(2), 135–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2014.918348 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2014.918348
Artigue, M., & Houdement, C. (2007). Problem-solving in France: Didactic and curricular perspectives. ZDM the International Journal on Mathematics Education, 39, 365–382. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-007-0048-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-007-0048-x
Ball, D.L., Thames, M.H., & Phelps, G. (2008). Content knowledge for teaching: What makes it special? Journal of Teacher Education, 59(5), 389–407. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487108324554 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487108324554
Ball, D.L., & Forzani, F. (2009). The work of teaching and the challenge for teacher education. Journal of Teacher Education, 60(5), 497–511. https://doi.org/10.1177/002248710934847 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0022487109348479
Bishara, S. (2016). Creativity in unique problem-solving in mathematics and its influence on motivation for learning. Cogent Education, 3(12), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2016.1202604 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2016.1202604
Bragg, L.A. (2015). Studying mathematics teacher education: Analysing the process of task variation on learning, Studying Teacher Education, 11(3), 294–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425964.2015.1065805 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17425964.2015.1065805
Brousseau, G. (1997). Theory of Didactical Situations in Mathematics. Kluwer.
Buchholtz, N., Leung, F. K., Ding, L., Kaiser, G., Park, K., & Schwarz, B. (2013). Future mathematics teachers’ professional knowledge of primary mathematics from an advanced standpoint. ZDM the International Journal on Mathematics Education, 45(1), 107–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-012-0462-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-012-0462-6
Carrillo-Yáñez, J., Climent, N., Montes, M., Contreras, L., Flores Medrano, E., Escudero Ávila, D., ... & Muñoz-Catalán, M. (2018). The mathematics teacher’s specialised knowledge (MTSK) model. Research in Mathematics Education, 20(3), 120–135. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2018.1479981 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2018.1479981
Cobb, P., Confrey, J., diSessa, A., Lehrer, R., & Shauble, L. (2003). Design Experiments in Educational Research. Educational Researcher, 32(1), 9–13. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X032001009 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X032001009
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2018). Research methods in education (8th edition). Routledge. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315456539
Creswell, J. W., & Guetterman, C.T. (2019). Educational Research: Planning, Conducting and Evaluating Qualitative and Quantitative Research (6th edition). Pearson.
Decker, S., & Roberts, A.M. (2015). Specific Cognitive Predictors of Early Math Problem-solving. Psychology in the Schools, 52(5), 477–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.21837 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.21837
Ding, M. (2016). Developing preservice elementary teachers’ specialized content knowledge: the case of associative property. International Journal of STEM Education, 3(9), 87-95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-016-0041-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-016-0041-4
Erkan, B., & Kar, T. (2021). Pre-service mathematics teachers’ problem-formulation processes: Development of the revised active learning framework. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 65, 100918. http://doi.org.10.1016/j.jmathb.2021.100918 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2021.100918
Fennema, E., & Franke, M. L. (1992). Teachers’ knowledge and its impact. In A. Grouws (Ed.) Handbook of research on mathematics teaching and learning: A project of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (pp. 147–164). Macmillan. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-60752-874-620251011
González-Martín, A., Bloch, I., Durand-Guerrier, V., & Maschietto, M. (2014). Didactic Situations and Didactical Engineering in university mathematics: cases from the study of Calculus and proof, Research in Mathematics Education, 16(2), 117–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2014.918347 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2014.918347
Goulding, M., Rowland, T., & Barber, T. (2002). Does it matter? teacher trainees’ subject knowledge in mathematics. British Educational Research Journal, 28, 689–704. https://doi.org/10.1080/0141192022000015543a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/0141192022000015543a
Hembree, R. (1990). The nature, effects, and relief of mathematics anxiety. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 21, 33-46. https://doi.org/10.2307/749455 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.21.1.0033
Henningsen, M., & Stein, M. (1997). Mathematical tasks and student cognition: Classroom-based factors that support and inhibit high-level mathematical thinking and reasoning. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 28(5), 524. https://doi.org/10.2307/749690 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/749690
Herbst, P.G. (2003). Using novel tasks in teaching mathematics: three tensions affecting the work of the teacher. American Educational Research Journal 40(1), 197–238. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312040001197
Kaiser, G., Blömeke, S., König, J., Busse, A., Döhrmann, M., & Hoth, J. (2017). Professional competencies of (pre-service) mathematics teachers–cognitive versus situated approaches. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 94, 161–182. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-016-9713-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-016-9713-8
Leavy, A., & Hourigan, M. (2018). Using Lesson Study to Support the Teaching of Early Number Concepts: Examining the Development of Pre-service Teachers’ Specialized Content Knowledge. Early Childhood Education Journal, 46(1), 47–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-016-0834-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-016-0834-6
Leikin, R., Zazkis, R., & Miller, M. (2017). Research mathematicians as teacher educators: focusing on mathematics for secondary mathematics teachers. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 21, 451–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-017-9388-9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-017-9388-9
Lendínez Muñoz, E.M., García García, F.J., & Lerma Fernández, A.M., (2023). Increase in self- efficacy in pre-service teachers through theory-based lesson study. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 27, 717–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-023-09597-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-023-09597-0
Livy, S., Herbert, S., & Vale, C. (2018). Developing primary pre-service teachers’ mathematical content knowledge: opportunities and influences. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 31, 279–299. https://doi.org/10.14221/ajte.2016v41n2.10 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-018-0252-8
Lynch, A.G., Lockwood, E., & Ellis, A.B. (2022). Comprehensive example generation: mathematicians’ uses of examples when developing conjectures, Research in Mathematics Education, 26(3), 363–385. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2022.2156586 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2022.2156586
Margolinas. C., & Drijvers, P. (2015). Didactical engineering in France: An insider’s and an outsider’s view on its foundations, its practice and its impact. ZDM the International Journal on Mathematics Education, 47(6), 893–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-015-0698-z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-015-0698-z
Masingila, J.O., Olanoff, D., & Kimani, P.M. (2018). Mathematical knowledge for teaching teachers: knowledge used and developed by mathematics teacher educators in learning to teach via problem-solving. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 21, 429–450. https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2022.2156586 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-017-9389-8
Morris, A., Heibert, J., & Spitzer, S. (2009). Mathematical knowledge for teaching in planning and evaluating instruction: what can preservice teachers learn? Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 40(9), 491–529. https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.40.5.0491 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.40.5.0491
Murphy, C. J. (2012). The role of subject knowledge in primary pre-service teachers approach to teach the topic of area. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 15, 187–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-011-9194-8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-011-9194-8
Palmér, H. (2016). Professional primary school teacher identity development: a pursuit in line with an unexpressed image. Teacher Development, 20, 682–700. https://doi.org/10.1080/13664530.2016.1202311 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13664530.2016.1202311
Pereira, P. (2005). Becoming a Teacher of Mathematics. Studying Teacher Education, 1, 63–82. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425960500040015 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17425960500040015
Putnam, R. T., Heaton, R., Prawat, R. S., & Remillard, J. (1992). Teaching mathematics for understanding: Discussing case studies of four fifth-grade teachers. Primary School Journal, 93(2), 213–228. https://doi.org/10.1086/461723 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1086/461723
Rivera, F. (2010). Visual templates in pattern generalization activity. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 73, 297–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-009-9222-0 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-009-9222-0
Rivera, F. (2013). Teaching and learning patterns in school mathematics. Psychological and pedagogical considerations. Springer. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-2712-0
Silver, E.A. (1997). Fostering creativity through instruction rich in mathematical problem-solving and problem posing. ZDM the International Journal on Mathematics Education, 29(75), 75–80.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-997-0003-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-997-0003-x
Taplin, M. (1998). Pre-service teachers’ problem-solving processes. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 10(3), 59–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03217058 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03217058
Weber, B-J., Breuer, J., & Lindmeier, A. (2023). How do school-related mathematical problems become relevant for pre-service teachers in mathematics courses at university? A qualitative interview study, Research in Mathematics Education, https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2023.2243261 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14794802.2023.2243261
Zazkis, R., & Leikin, R. (2010). Teachers’ opportunities to learn mathematics through teaching. In Zazkis & Leikin (Eds.), Learning through Teaching Mathematics: Mathematics Teacher Education (pp. 3–21). Springer. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3990-3_1
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Rimma Nyman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









